According to ET News, Apple is now producing final prototypes of iPads with OLED displays, with the device having a lightweight design and improved display quality.
The prototypes are reportedly being produced with Korean display partners, Samsung and LG Display, allowing Apple to undertake a series of tests. It is also believed that the Cupertino-based company is developing a special coating to increase the display’s durability, made necessary due to its slimness.
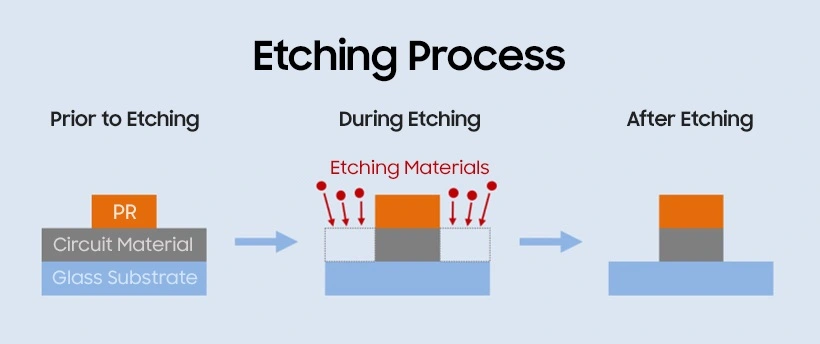
The report also reveals that Apple is focusing on giving the iPad OLED a lighter design and “unrivalled picture quality”, in part facilitated by a dry etching process that significantly reduces the weight of the display.
Apple will also introduce the dry engraving process in the iPad OLED display for the first time. Dry etching of the display is a process of removing unnecessary parts using chemical technology when creating thin-film transistor (TFT) circuit diagrams. The display can be engraved to make it thinner and lighter.
The company did not use this etching process to make the iPhone’s OLED panel lighter as it already offered a weight reduction compared to previous iPhones with LCD displays, which would also have resulted in increased costs .
In addition to this, Apple is developing special coatings to increase the life of the thin display panel. Samsung and LG Display are expected to supply the OLED panels.
Apple is producing final prototypes of iPad OLEDs with major national display partners . As this is the first time that OLED has been used in a tablet, Apple is creating several prototypes and repeating the testing process several times.
Why is this a more advanced process?
Engraving is the process of removing unwanted material from a display module to reduce its weight. Conventional OLED manufacturing uses a wet etching process, while the more advanced approach is dry etching.
Here’s how Samsung Display explains the difference when offering the dry engraving process to customers like Apple:
Wet etching uses a solution to induce a chemical reaction to cut out a part, while dry etching removes specific parts using reactive gases and ions.
Wet engraving, compared to its dry counterpart, is cheaper, faster and easier. However, it is less accurate than the dry method and carries the risk of contamination due to the use of chemicals in the process. Dry engraving is best suited for creating a microcircuit due to its ability to easily target specific parts for engraving. However, it is expensive, complex, and slow to process.
Dry etching is often referred to as plasma etching. In this process, an etching gas is injected into the vacuum chamber where the substrate is placed, then electrical energy is supplied to the chamber to create plasma. Next, the ions that obtain high levels of kinetic energy from the ionized gas are accelerated by the electrodes on the substrate so that the atomic bond in the circuit material is broken, which allows for etching. Dry etching is the preferred method used for most of the microcircuit designs required today for high resolution displays.



Recent Comments